Thin film solar cell structure
Different types of thin-film solar cells have different structures, so that their use efficiency is also different. For thin-film solar cells with different compositions, there will be different applications.
Silicon-based thin-film solar cells mainly include a reflective layer, a back contact layer, a crystalline silicon layer, a transparent conductive layer, and glass. The substrate is mainly glass, special plastics, ceramics, stainless steel, etc. The thickness of the silicon crystal layer is 350~450um, which is usually formed by pulling or casting silicon ingots, so the consumables are large, the raw material utilization rate is low, and the use of ultrasonic atomization spraying can greatly improve this shortcoming. In addition, ultrasonic spraying can also maintain good uniformity and uniformity, and the operation is simple and easy to use.
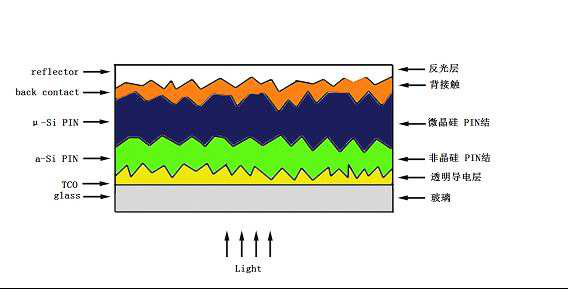
Figure 1 Silicon-based thin-film solar cell structure
Inorganic compound thin-film solar cells mainly include electrode plates, back contact layers, absorber layers, window layers, transparent conductive layers, and glass. The inorganic absorption layer and the window layer are mainly cadmium telluride, copper indium selenium, gallium arsenide and other chemical solvents, which can absorb about 90% of the solar photons on the 0.5um thick inorganic absorption layer. The thickness of the film is mainly between 2-3um, but due to the scarcity of raw materials and high cost, the original air spray will reduce the utilization rate of raw materials and cost high. If the method of ultrasonic spraying is used, the utilization rate of raw materials can be improved and the cost can be reduced.
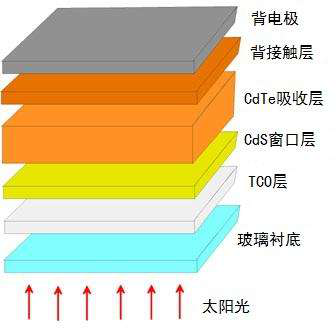
Figure 2 Inorganic thin-film solar cell structure
Organic thin film solar cells mainly use small organic molecules or organic polymers to directly or indirectly convert solar energy into electrical energy. Organic thin film solar cells mainly include single-layer Schottky cells, double-layer p-n heterojunction cells, and bulk-phase heterojunction cells with P-type and N-type semiconductor network interpenetrating structures. Polymers in organic thin-film solar cells absorb photon energy to generate excitons, which dissociate into free carriers to generate photocurrents. However, in the current experiment, because the dissociation efficiency of excitons is too low, the conversion efficiency is very low, and the short life is short. If ultrasonic spraying can be used, the dissociation efficiency of excitons can be improved, and the service life of the battery can be extended.
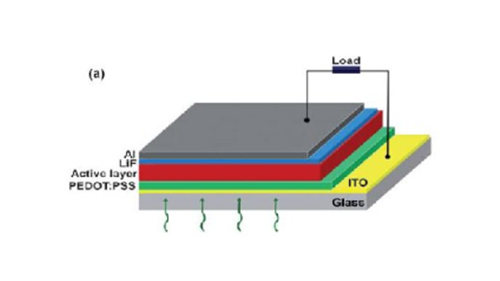
Figure 3 Organic thin film solar cell structure
The above is the composition analysis of three common thin-film solar cells. For different coatings and solutions, ultrasound can give customized solutions.
Spray waterproof and breathable film base is mesh ultrasonic coating – Cheersonic